FXB4-36/70SB
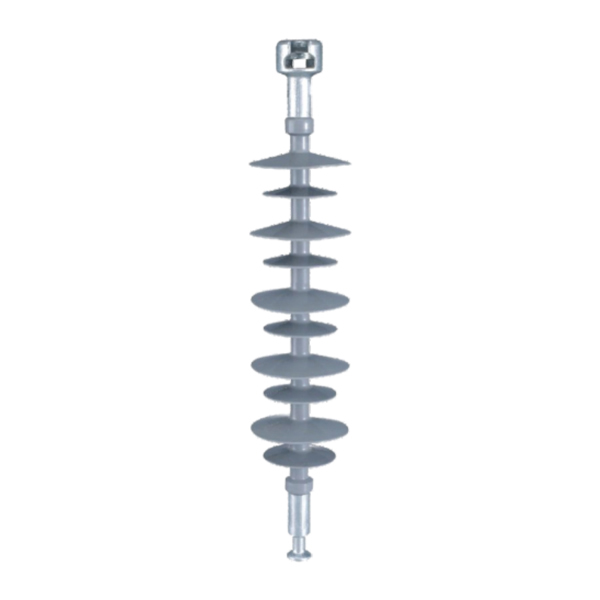
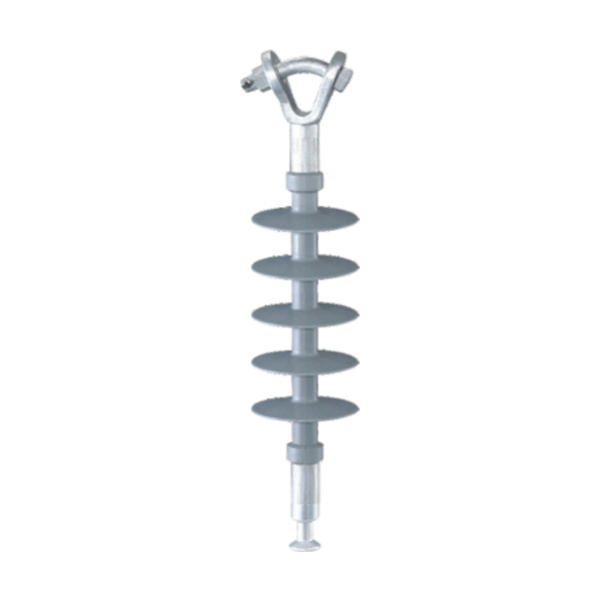
As an alternative to ceramics, composite materials were developed for use in insulators for transmission systems.
Description
General
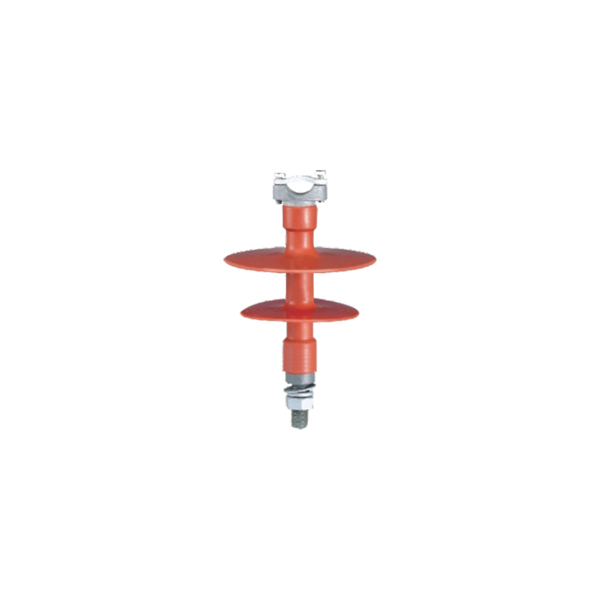
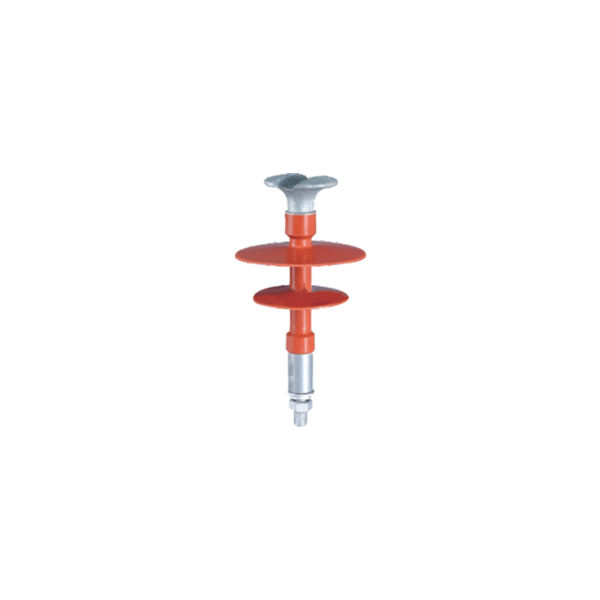
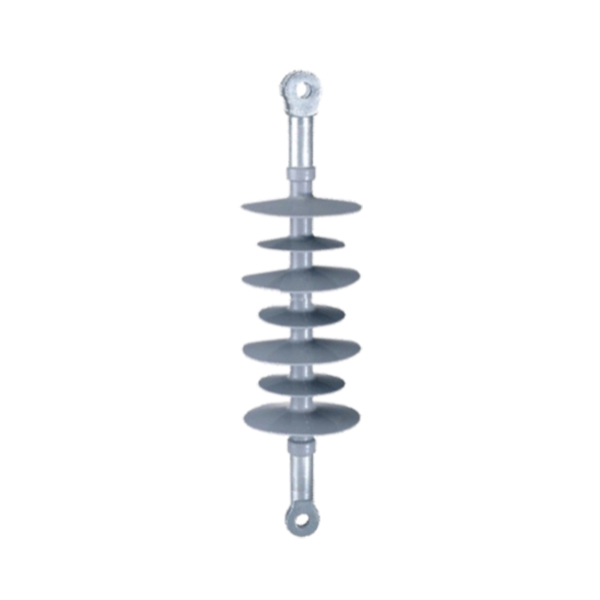
As an alternative to ceramics, composite materials were developed for use in insulators for transmission systems. Such composite insulators are also referred to as non-ceramic insulators(NCI) or polymer insulators, and usually employ insulator housings made of materials such as ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), polytetro fluoro ethylene (PTFE), silicone rubber, or other similar materials. Compared with the conventional insulators manufactured homogeneously from the material ceramic or glass,composite insulators consist of two components of different materials. A number of composite insulators made from lighter weight polymeric materials have been developed for use in such high voltage installations. Such composite insulators generally include a fiberglass rod having a number of weather sheds constructed of a highly insulating polymeric material attached to the rod along its length. Composite insulators including shield layers of a synthetic material are given preference mainly because the shield layer of a synthetic material, particularly silicone, is hydrophobic, i.e. the insulators employed mostly outdoors are highly water repellant which is conducive to repelling dirt and thus to low leakage current losses. And also, this is a lightweight structure which facilitates assembly. Composite insulators are generally produced by preparing the screens individually and then fitting the required number of them onto a shank coated with extrudate and vulcanizing them with the coat, or by centrally placing a rod with a predetermined number of screens in a two-part mould and injecting all the screens at once. Composite insulators for high-tension use must conform to specific electrical requirements. The carrier rod must be electrically insulating in its axial direction and the insulating layer must be secured thereto in a manner that no electrical conduction can occur at the seam between the insulating cover and the interior carrier rod. The insulating cover performs several functions including providingresistance to weathering, UV, ozone, etcetera. The cover is also required to have good mechanical resistance to cold and good electrical tracking resistance. Desirably the insulating cover should be flexible, halogen-free and flame retardant.
Conditions ofApplication
Ambient environment:
a) Temperature:-40℃≤T≤ 40℃
b) Altitude above sea level: ≤1500m
c) Max.wind speed: ≤35m/s
d) Earthquake intensity:≤8 degree
e) Frequency ofAC power: ≤100Hz
OThe filthy area should be indicated.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.